- Project Objectives
1.1 Location Tracking:
- Utilize a GPS module to capture real-time coordinates of the dog’s location.
1.2 Pulse Rate Monitoring:
- Integrate a pulse rate sensor to measure the dog’s pulse in real-time, promoting health monitoring.
1.3 Remote Monitoring:
- Implement Blynk IoT software to enable users to remotely monitor their dog’s location and health data.
1.4 Alert System:
- Develop an alert system for notifying users in case of predefined events, such as the dog leaving a designated area or experiencing abnormal pulse rates.
- Technologies Integrated
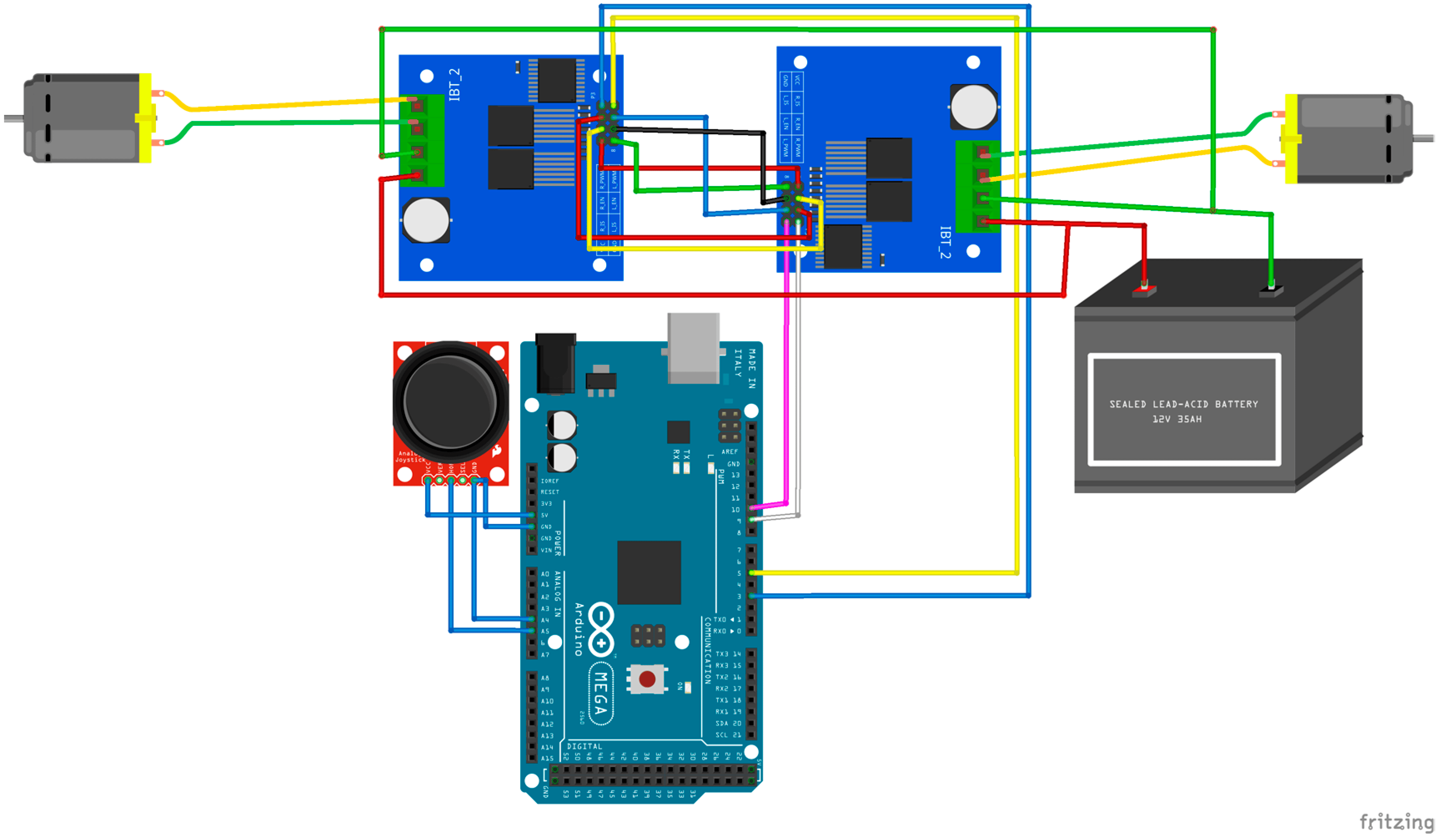
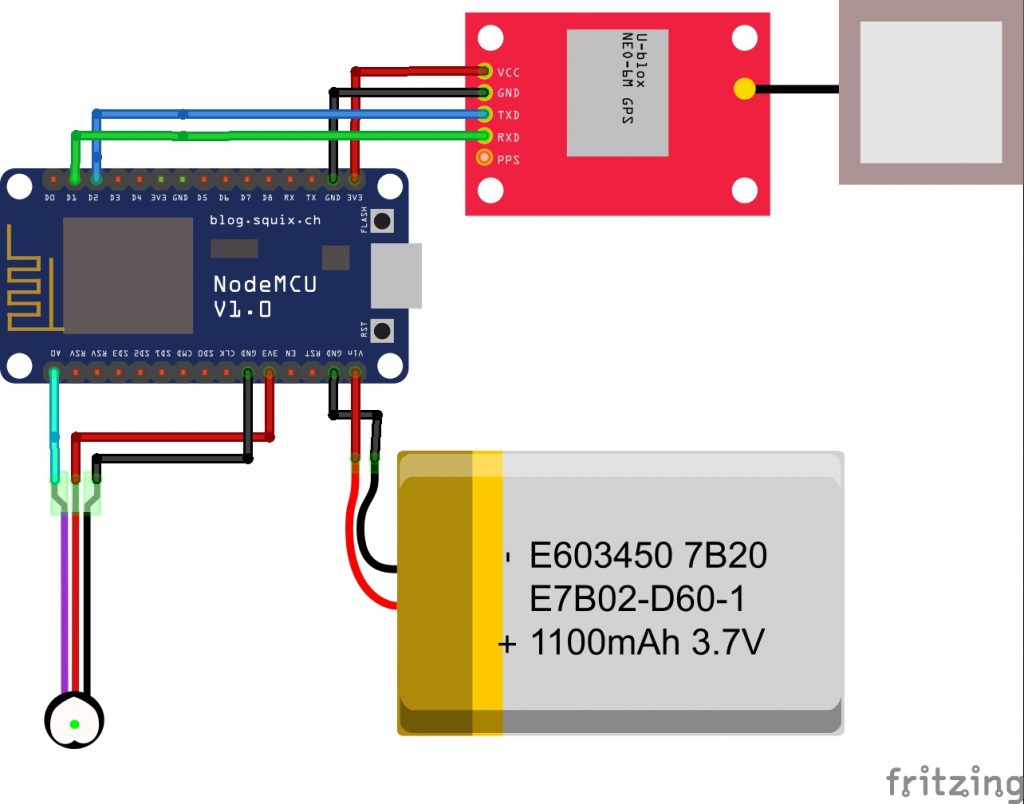
2.1 NodeMCU:
- Serves as the central processing unit, responsible for data processing and communication among hardware components.
2.2 GPS Module:
- Captures real-time location data, enabling accurate tracking of the dog’s movements.
2.3 Pulse Rate Sensor:
- Measures the dog’s pulse, providing essential health-related information.
2.4 Blynk IoT Software:
- Creates a user-friendly interface for remote monitoring, enhancing accessibility for pet owners.
- The Dog Band project is versatile, allowing adjustments and enhancements for specific applications:
- Security Access Control.
- Pet Tracking Systems.
Conclusion
This project exemplifies the integration of different technologies, such as GPS and IoT, to create a simple yet effective Dog Band system. The combination of hardware components and software tools offers pet owners a valuable tool for monitoring and ensuring the well-being of their dogs.
CODE
#include <TinyGPS++.h>
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
#define BLYNK_TEMPLATE_ID "TMPL3Jee8U12h"
#define BLYNK_TEMPLATE_NAME "Dog band"
#define BLYNK_PRINT Serial
#include "MAX30100_PulseOximeter.h"
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
#include <BlynkSimpleEsp8266.h>
char auth[] = "sOdeFNHZo2fxa_sGoDKWUYjXyij7l4y4"; // change it to your auth code
char ssid[] = "Oppo A53"; // change it
char pass[] = "NASA@7011"; // change it
int PulseSensorPurplePin = 0; // Pulse Sensor PURPLE WIRE connected to ANALOG PIN 0
//int LED13 = 2; // The on-board Arduion LED
int Signal; // holds the incoming raw data. Signal value can range from 0-1024
int Threshold = 550; // Determine which Signal to "count as a beat", and which to ingore
static const int RXPin = 4, TXPin = 5; // GPIO 4=D2(conneect Tx of GPS) and GPIO 5=D1(Connect Rx of GPS
static const uint32_t GPSBaud = 9600; //if Baud rate 9600 didn't work in your case then use 4800
TinyGPSPlus gps; // The TinyGPS++ object
WidgetMap myMap(V0); // V0 for virtual pin of Map Widget
SoftwareSerial mygps(RXPin, TXPin);
//BlynkTimer timer;
float latitude; //Storing the Latitude
float longitude; //Storing the Longitude
float velocity; //Variable to store the velocity
float sats; //Variable to store no. of satellites response
String bearing;
unsigned int move_index = 1;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(115200);
mygps.begin(GPSBaud);
Blynk.begin(auth, ssid, pass);
//timer.setInterval(5000L, checkGPS);
}
void checkGPS()
{
if (gps.charsProcessed() < 10)
{
Serial.println(F("No GPS detected: check wiring."));
Blynk.virtualWrite(V3, "GPS ERROR"); // Value Display widget on V3 if GPS not detected
}
}
void loop()
{
while (mygps.available() > 0)
{
// sketch displays information every time a new sentence is correctly encoded.
if (gps.encode(mygps.read()))
if (gps.location.isValid() )
{
sats = gps.satellites.value(); //get number of satellites
latitude = (gps.location.lat()); //Storing the Lat. and Lon.
longitude = (gps.location.lng());
velocity = gps.speed.kmph(); //get velocity
bearing = TinyGPSPlus::cardinal(gps.course.value()); // get the direction
Serial.print("SATS: ");
Serial.println(sats); // float to x decimal places
Serial.print("LATITUDE: ");
Serial.println(latitude, 6); // float to x decimal places
Serial.print("LONGITUDE: ");
Serial.println(longitude, 6);
Serial.print("SPEED: ");
Serial.print(velocity);
Serial.println("kmph");
Serial.print("DIRECTION: ");
Serial.println(bearing);
Blynk.virtualWrite(V2, String(latitude, 6));
Blynk.virtualWrite(V3, String(longitude, 6));
Blynk.virtualWrite(V4, sats);
Blynk.virtualWrite(V5, velocity);
Blynk.virtualWrite(V6, bearing);
myMap.location(move_index, latitude, longitude, "GPS_Location");
}
Serial.println();
}
Signal = analogRead(PulseSensorPurplePin); // Read the PulseSensor's value.
// Assign this value to the "Signal" variable.
Serial.println(Signal);
Blynk.run();
//pulsense = analogRead(A0) - 440;
Serial.println(Signal);
Blynk.virtualWrite(V1, Signal);
//Blynk.virtualWrite(V2, String(lat_val, 6));
//Blynk.virtualWrite(V3, String(lng_val, 6));
if(Signal > Threshold){ // If the signal is above "550", then "turn-on" Arduino's on-Board LED.
Blynk.logEvent("Pulse Rate High", String("Pulse rate is very high. Check your pet."));
} else if(Signal < 50) {
Blynk.logEvent("Pulse Rate Low", String("Pulse rate is very low. Contact a doctor. ")); // Else, the sigal must be below "550", so "turn-off" this LED.
}
//Blynk.logEvent("event_code", String("High TemperatureDetected! Tº: ") + temp);
}